Thin Film Deposition丨Principles and Applications of Magnetron Sputtering Technology
What is magnetron sputtering?
Magnetron sputtering is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process that belongs toOne of the vacuum deposition processesIt is widely used in industrial coating because of its low deposition temperature, good film quality, uniformity, fast deposition speed and the ability to produce large areas of uniform and dense films. It is widely used in industrial coating because of its many advantages such as low deposition temperature, good film quality, good uniformity, fast deposition speed, and the ability to prepare large-area uniform and dense hard films.
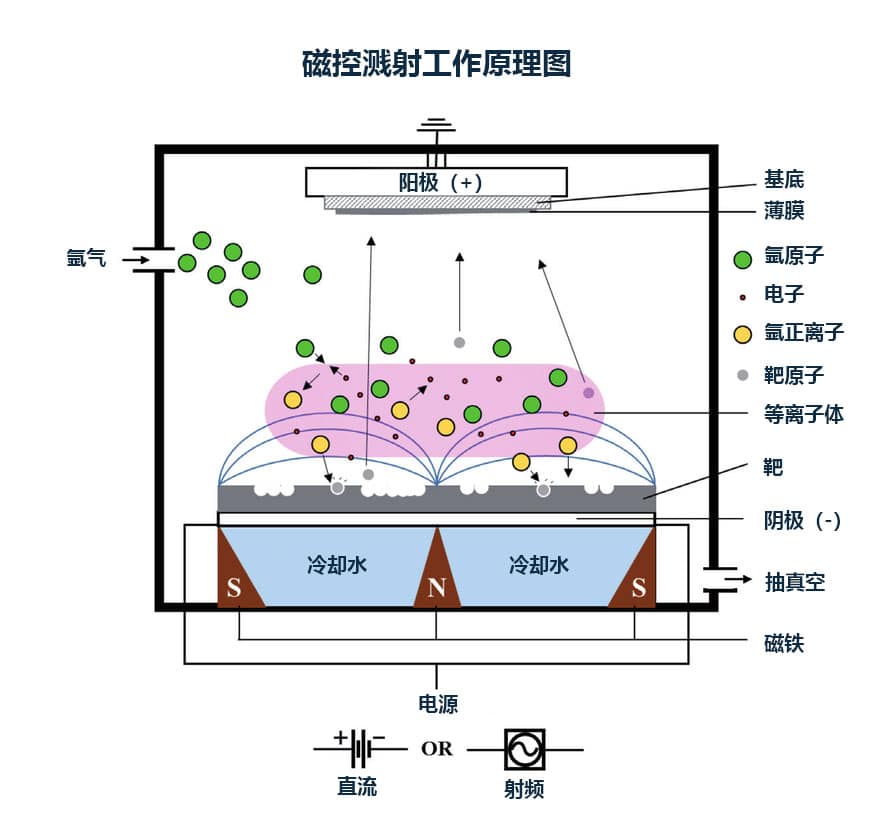
The name "magnetron sputtering" comes from the use of a magnetic field to control the behavior of charged ion particles during magnetron sputtering deposition. The process requires a high vacuum chamber to create a low pressure environment for sputtering.First, putThe gas containing the plasma (usually argon) enters the chamber.A high negative voltage is applied between the cathode and anode to initiate the ionization of the inert gas. The positive argon ions from the plasma collide with the negatively charged target. Each collision of the energetic particles causes atoms from the target surface (target) to be ejected into the vacuum environment and propelled onto the substrate surface.Strong magnetic fields produce high plasma densities by confining electrons near the target surface (target), increasing the deposition rate and preventing damage to the substrate from ion bombardment. Most materials can be used as targets for sputtering processes because magnetron sputtering systems do not require melting or evaporationSource Material.
Advantages of magnetron sputtering
Magnetron sputteringBetter than othersthin film deposition technology, as it allows the preparation of a large number of films at a very low cost.It is also very suitable for high melting point materials that cannot be evaporated, and is a technology that can form very dense films with good adhesion.
- Environmental Protection
- Fast deposition rate
- Comprehensive material coverage
- Low temperature environment
- High film purity and good denseness
- High viscosity film, good film-to-substrate bonding
- Simultaneous sputtering of different materials on substrates
- Easy to realize industrialization, can obtain very good uniformity of film on large area substrate
Application of magnetron sputtering
- Various functional films: films with special functions such as absorption, transmission, reflection, refraction, polarization, etc. For example, low-temperature deposited silicon nitride permeability-enhancing films used to improve the photovoltaic conversion efficiency of solar cells.
- Exterior decoration field: total reflection film and translucent film, cell phone case, mouse, etc.
- In microelectronics, it can be used as a non-thermal coating technology, mainly for chemical vapor deposition (CVD), to obtain large-area uniform films.
- Optical field: optical film (such as translucent film), low radiation glass, transparent conductive glass, etc.
- Machining industry: Surface deposition technologies such as surface functional films, super hard films and self-lubricating films have been developed greatly from the beginning. These films can effectively improve the surface hardness, compound toughness, wear resistance, high temperature chemical stability and service life of coated products.
- In addition to the above-mentioned areas where magnetron sputtering has been applied extensively, it also plays an important role in the research of high-temperature superconducting thin films, ferroelectric thin films, giant magnetoresistive thin films, thin film light-emitting materials, solar cells, and memory alloy thin films.
Common Sputtering Materials
Magnetron sputtering can process materials:
ITO (Indium Tin Oxide), IGZO (Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide), SiO2 (Silicon Dioxide), Mo (Molybdenum), Ti (Titanium), Al (Aluminum), Au (Gold), Pt (Platinum), Ag (Silver), W (Tungsten), Cu (Copper), Co (Cobalt) and other types of metal thin films, compounds materials.
We offerMagnetron sputtering / thin film deposition / micro and nanostructure processing design services, Feel free to leave a message to inquire.
Related Products
Related Reading
Micro and Nano Processing | E-paper micro-cups and micro-chamber structure preparation
Microfabrication | E-paper microcups microchamber type structure preparation For when
Micro and Nano Processing | MEMS Fine Processing (III)
Micro and Nano Processing | MEMS Fine Processing (III) MEMS-oriented
Micro and Nano Processing | MEMS Micro Energy System Preparation
Micro-Nano Processing | MEMS Micro-Energy Device System Preparation With the micro-computer