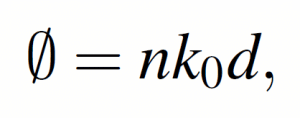
Introduction to super-surface lenses (metalenses) 丨Design principles, applications and processing methods
What is a superlens?
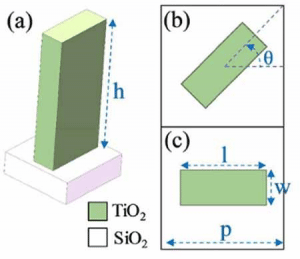
The design principle of superlens and phase regulation method
- Resonance phase controlIt is the phase abrupt change by changing the resonant frequency, which is controlled by the geometry of the nanoscale structure. However, because resonant phase hypersurfaces are usually made of metal materials such as gold, silver, and aluminum, they inevitably cause ohmic losses and make it difficult to achieve high-efficiency optical field modulation. And the super-surface lens made of low-loss dielectric material can effectively solve this problem.
- Propagation phaseis due to the fact that electromagnetic waves produce optical range differences during propagation, and phase modulation can be achieved by using this property. The phase regulation (φ) is regulated by the optical range difference, where the wavelength is λ , the effective refractive index of the medium is n, and the electromagnetic wave propagates at a distance d (the height of the structure) in a uniform medium, where k0=2π/λ is the free space wave vector, then the accumulated propagation phase of the electromagnetic wave can be expressed as

- Geometric Phasesis an artificial control of phase gradients or distributions by adjusting the rotation angle of micro and nano structures with the same dimensions to achieve abrupt phase changes of optical waves, thus greatly reducing the complexity of designing and processing hypersurfaces. The advantage of geometric phase modulation is that it is not affected by material dispersion, structure size, and structural resonance.

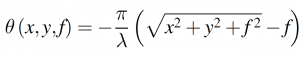
Current Research Status and Applications of Superlens
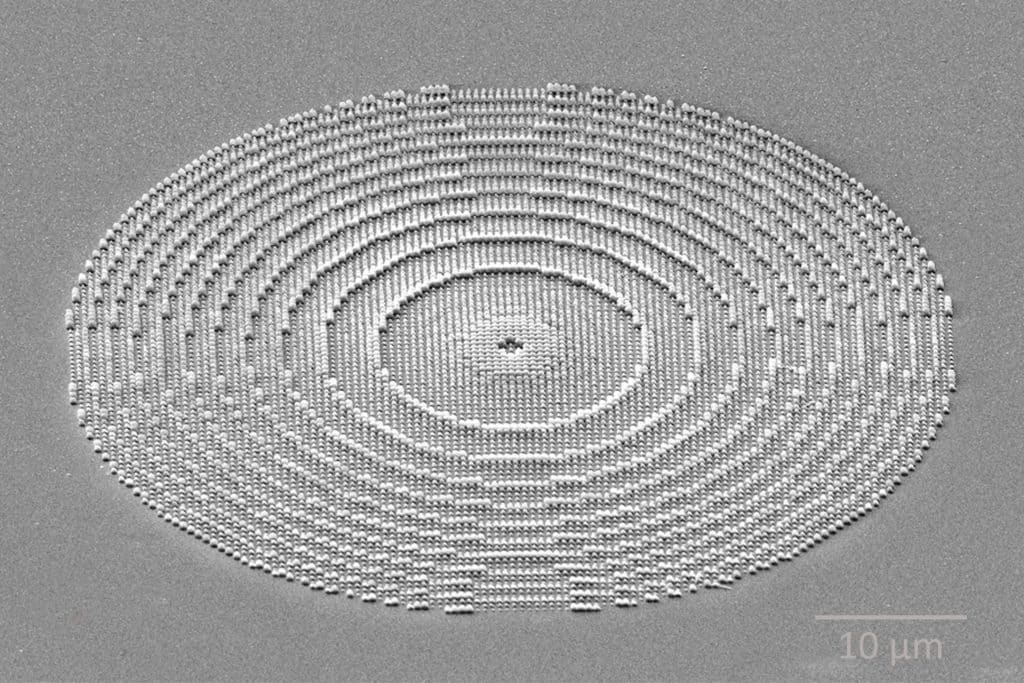
High numerical aperture (NA) superlenses
Achromatic Superlens (AML)
As a diffractive optical device, superlenses, like other diffractive lenses, suffer from severe chromatic aberrations of their own. Although these lenses can operate in a wide range of optical wavelengths, the existence of chromatic aberration severely limits the application in optical focusing and imaging. Especially for optical super-resolution planar superconfiguration lenses, there are many challenges to eliminate chromatic aberrations in planar superconfiguration lenses while achieving super-resolution point optical diffusion.
- Multi-wavelength achromatic superlenses based on low-loss coupled rectangular dielectric resonators
- Broadband achromatic superlenses: building blocks and intensity distribution of different superlenses
- Narrow-band achromatic superlens
Multifocal Superlens
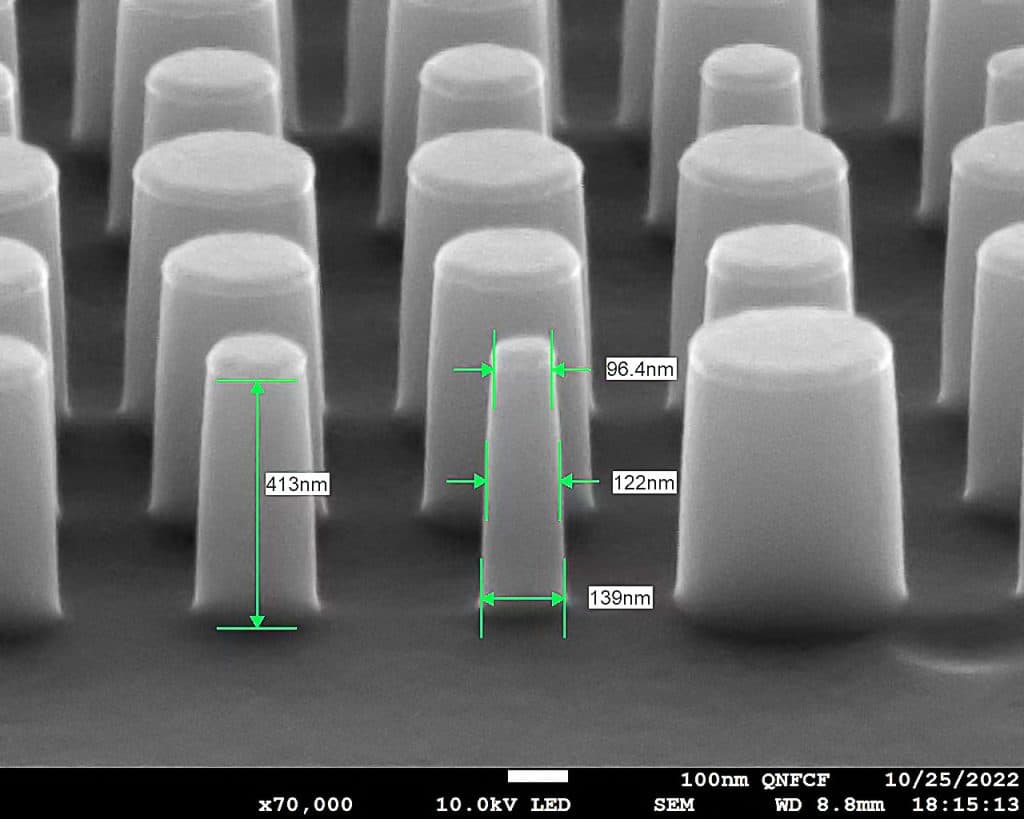
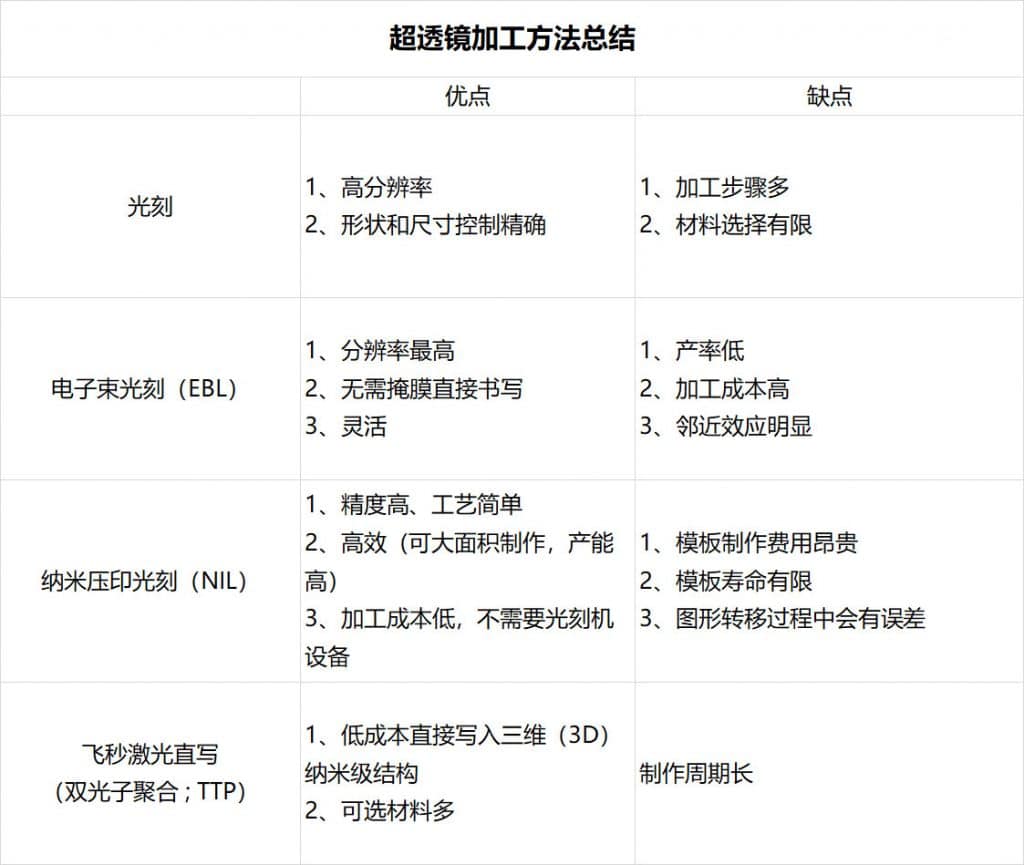
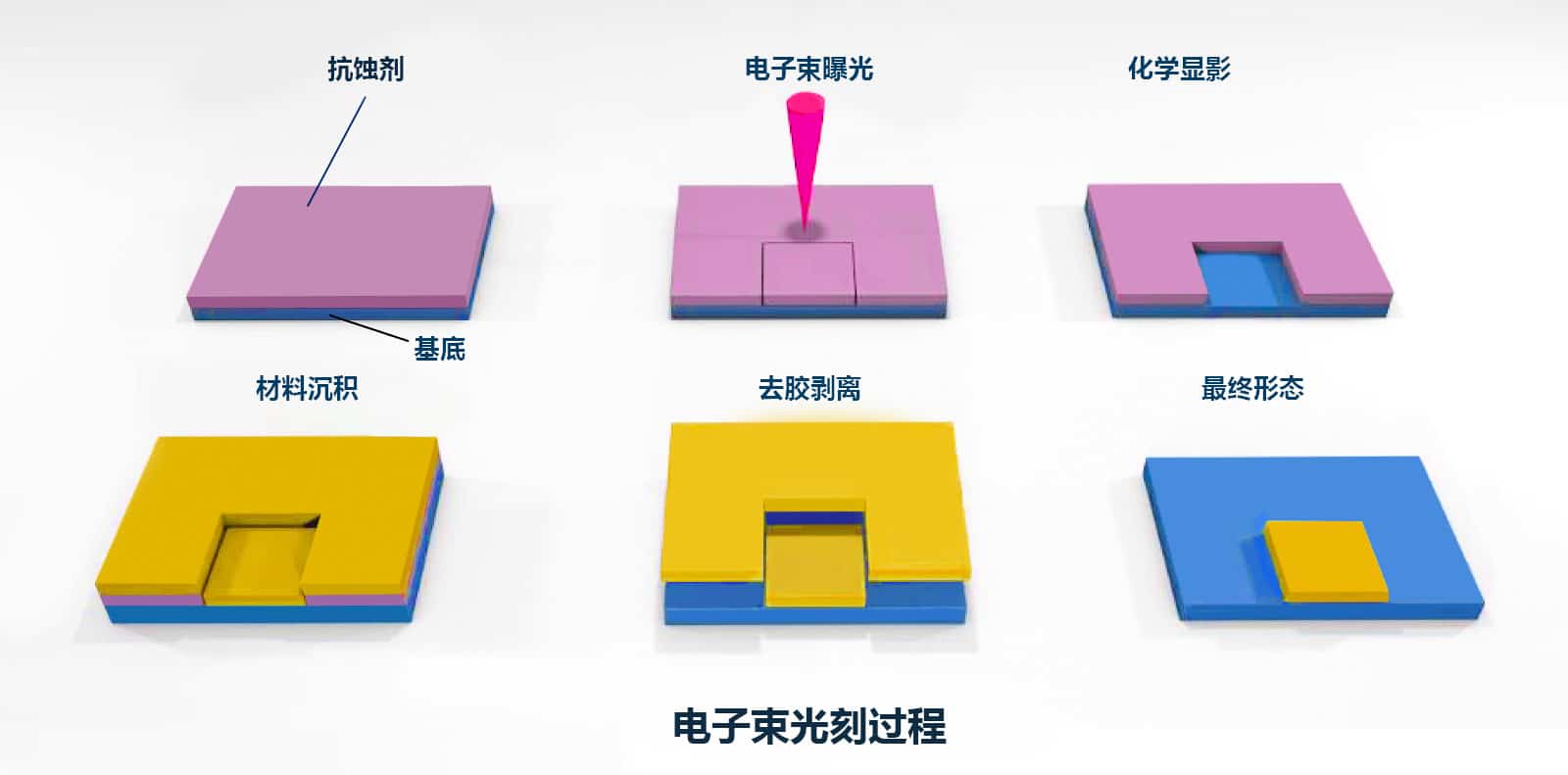
Superlens processing method
Femtosecond Laser Direct Writing Lithography
Nanoimprinting technology (in-depth knowledge)
We offerMicrolens arrays / Nanoimprinting / Micro and nanostructure processing design services, Feel free to leave a message to inquire.
Related Products
Related Reading
Micro and Nano Processing | MEMS Fine Processing (I)
Micro and Nano Processing | Introduction to MEMS Processing (I) Micro System (Mi)
Micro and Nano Processing | Introduction to Dry Etching
Micro and Nano Processing | Dry Etching Process Introduction Etching technology is divided into: wet process
Micro and Nano Processing | Process Overview
Micro and Nano Processing | Thin Film Deposition, Photolithography, Etching Overview Nanofabrication Division